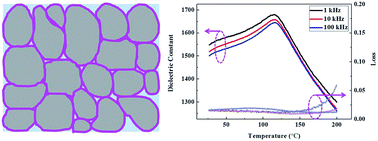
B site vacancies introduce cation disorder in the perovskite lattice and are in fact one of the main driving forces for relaxor behaviour in barium titanate batio 3 bt based ferroelectrics.
Ceramic defect 2 vacancie.
Schottky defect occurs when oppositely charged atoms cation and anion leave their corresponding lattice sites and create a pair of vacancy defects.
There is a shift for b 1g e g and a 1g modes of the tio 2 x ceramics which may be related to lattice deformation caused by oxygen vacancies and ti 3 defects.
However such oxygen vacancies are part of the defect complexes 58 acting differently than the free vacancies.
Schottky defect point defect in ionic crystal ceramic it is one type of point defect that occurs in ionic crystals ceramics.
Concentration of intrinsic defects the concentration of defects is given as the fraction of the total number of atoms n as following.
So one schottky defect leads to the formation of two vacancies.
22 point defects 2.
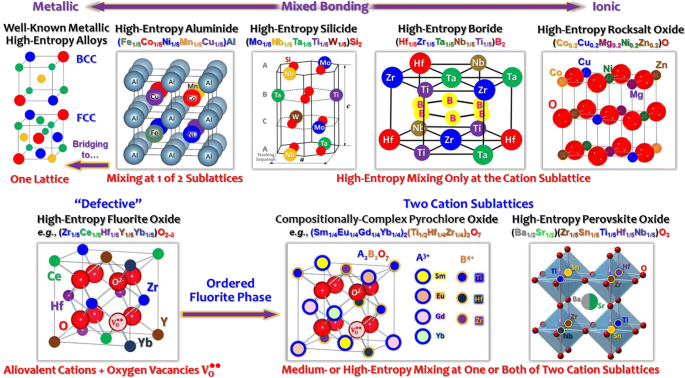
Defects in particular vacancies play a crucial role in substituted perovskite systems influencing the structural features that underpin ferroelectricity.
2 ceramic crystal structures.
Vacancies and in al2o3 the schottky defect is a quintuplet.
Schottky defect occurs when oppositely charged atoms cation and anion leave their corresponding lattice sites and create a pair of vacancy defects.
Comparison of the total energy differences with respect to the m phase introduced by an oxygen vacancy and a substitutional silicon in hfo 2 for 6 25 f u doping or vacancy concentration 23.
The peak around 234 cm 1 could be associated with the multi phonon mode of the second order raman scattering in rutile structure 22.
The relevant imperfection determining the mechanical properties of ceramics are point defects or dislocations or both.
Defect which conserves the number of lattice sites.