Great care must be taken to ensure the polarity markings are observed when inserting these capacitors into circuits otherwise damage to the component and more importantly to the remainder of the circuit board can result.
Ceramic capacitor polarity identification.
Ceramic capacitors have no polarity.
They are classified into 3 types they are fixed capacitor polarised capacitor and a variable capacitor.
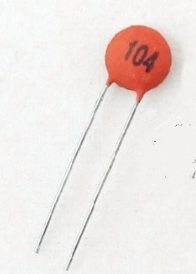
Ceramic capacitors are usually smaller than your thumb and attach to the circuit with two pins.
This is the process followed in capacitor polarity identification that can be done.
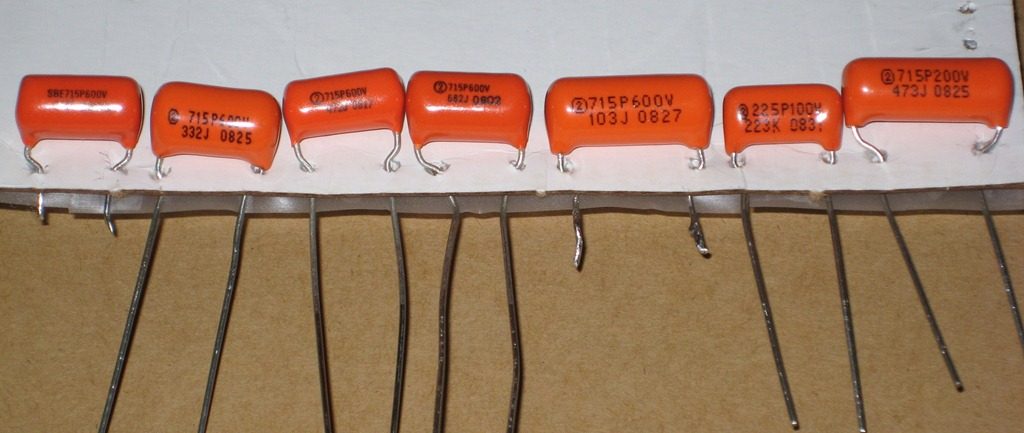
Used in many applications they typically range from 1 nf to 1 µf and occasionally up to 100 µf.
If you have to worry about the polarity at all when it comes to c.
The value of the capacitor is indicated in picofarads.
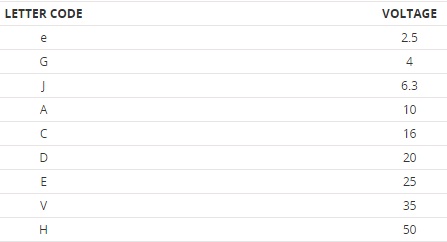
The markings on a ceramic capacitor are more concise in nature since it is smaller in size as compared to electrolytic capacitors.
Thus for such concise markings many different types of schemes or solutions are adopted.
A capacitor is an electronic component that stores energy in electric form when charged and is also known as a two terminal passive component or a condenser measured in farads f it consists of two metallic parallel plates which are separated by a gap filled with a dielectric medium.
In case of non polarized capacitors it is marked as np on the capacitor for example npa or npr where np stands for non polarized a stand for axial and r stands for radial.
One important marking for polarised capacitors is the polarity.
The large capacitors in an antique radio typically range from 1 200 µf.
But there must be some identification for the non polarized capacitors.